

| Harrisburg International Airport is the
primary technology validation site for the NGS airport survey program.
We have ongoing experiments with digital photogrammetry, hyperspectral,
and LIDAR data to evaluate the usefulness of these types of data for supporting
airspace analysis.
The image at left is a shaded relief representation of a 1 meter digital surface model (DSM) constructed by NGS engineers using airborne LIDAR data. The spatial extent is approximately 800 by 1000 meters. The prominent linear feature at the bottom of the image are the approach lights at runway end 13, which are located along the north bank of the Susquehanna River. The image at right is a 1 meter bin constructed by NGS engineers depicting the mean LIDAR elevation measured within 1 meter groundels. The black pixels represent 1 meter groundels with no LIDAR measurement. The raw data were acquired in the Fall of 1998 using the NASA Airborne Topographic Mapper II aboard a NOAA Twin Otter aircraft. |
|
Shaded relief image of runway 13
|
|
| In the Fall of 1998 and the Summer of 1999 NGS acquired AVIRIS hyperspectral data of the airport. The image below at left is a 3 channel composite of runway end 13. The image below at right is a segmentation designed to separate the asphalt runway from the concrete taxiways. The yellow pixels represent an attempt to auto-identify the paint stripes delineating the runway edges. Such classifications of hyperspectral data may prove useful in automatically identifying aircraft ground movement areas. |
|
|
|
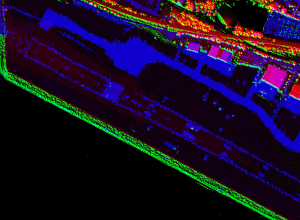
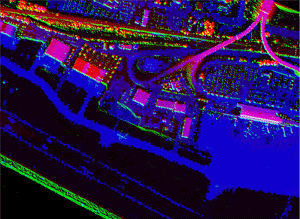
| NGS has developed a methodology to georegister the low altitude AVIRIS data collected at Harrisburg Airport. Once the data has been accurately positioned, data from other sensors can be merged with the AVIRIS data. The images below show a pixel level data fusion of the runway using AVIRIS channel 24, a LIDAR shaded relief image, and a LIDAR TIN depicting heights. For best results, the image should be viewed using Chromadepth 3D high definition glasses. |
Pixel level data fusion at Harrisburg Airport
Click images to see a full resolution view
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
[NOAA Main Page] [NOS Main Page] [NGS Main Page] |
 |
National
Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
National Ocean Service / National Geodetic Survey Remote Sensing Division This page updated on March 28, 2000 |